Thread, do mechanical daily interaction, for a long time domestic and foreign, metric inch, straight cone, sealed unsealed, inner and outer, 55 degrees 60 degrees In short, it is often messed up, and it is checked once from start to finish. I can summarize it here and hope it helps.
My method is to print it out and put it on the table, and use it to view it at any time. It will naturally be remembered after a long time.
NPT is a general purpose American standard tapered pipe thread with a tooth angle of 60 °
PT teeth are British tapered threads with a tooth angle of 55 ° and are most commonly used in sealing. The inch pipe thread is a fine thread, because the thread depth of the coarse thread is large, which will seriously reduce the strength of the pipe with the outer diameter of the cut thread.
PF teeth are parallel threads for pipes.
G is a 55-degree non-threaded sealed pipe thread and belongs to the Wyeth thread family. Marked as G represents cylindrical thread, G is the general name of pipe thread (Guan), the division of 55 and 60 degrees belongs to functional
ZG is commonly known as pipe cone, that is, the thread is processed from a conical surface, and the general water pipe joints are like this. The old national standard is marked as Rc
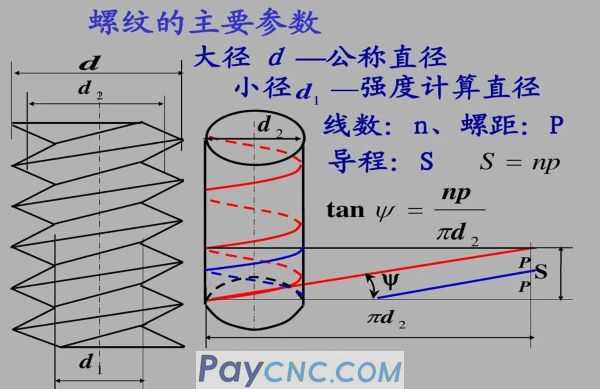
The metric thread is represented by the pitch, and the US and British threads are represented by the number of threads per inch. This is their biggest difference. The metric thread is a 60 degree equilateral tooth shape, the inch thread is an isosceles 55 degree tooth shape, and the American thread 60 degrees. Metric units are used for metric threads, and American and British threads are used for British units.
The pipe thread is mainly used to connect the pipe, and the internal and external threads are closely matched, there are two kinds of straight pipe and conical pipe. The nominal diameter refers to the diameter of the connected pipe. Obviously, the major diameter of the thread is larger than the nominal diameter.
1/4, 1/2, 1/8 are the nominal diameter of inch thread, the unit is inch.
1. Inch uniform thread
Widely used in inch countries, this type of thread is divided into three series: coarse tooth series UNC, fine tooth series UNF, extra fine tooth series UNFF, plus a fixed pitch series UN.
Marking method: thread diameter—number of teeth per inch series code—accuracy grade
Example: Coarse teeth series 3 / 8—16UNC—2A
Fine teeth series 3 / 8—24UNF—2A
Extra fine teeth series 3 / 8—32UNFF—2A
Fixed pitch series 3 / 8—20UN—2A
The first digit 3/8 represents the outer diameter of the thread, the unit is inch, converted to the metric unit mm multiplied by 25.4, that is, 3/8 × 25.4 = 9.525mm; the second and third digits 16, 24, 32, 20 are Number of teeth per inch (number of teeth on 25.4mm length); the character codes UNC, UNF, UNFF, UN after the third digit are series codes, and the last two digits 2A are accuracy grades.
2. Conversion of 55 ° cylindrical pipe thread
The 55 ° cylindrical pipe thread is from the inch series, but it is widely used in the metric and inch countries. It is used to connect the pipe joints and pipes of the liquid, gas, and installation wires. However, the code of each country is different. The foreign codes in the table (comparison table) have been converted into Chinese codes, and the 55 ° cylindrical pipe thread codes of various countries are listed in the table below.
Country code
China G
Japan G, PF
UK BSP, BSPP
France G
Germany R (internal thread), K (external thread)
Former Soviet Union G, TPУБ
ISO Rp
3. Conversion of 55 ° conical pipe thread
A 55 ° conical pipe thread refers to a thread with a tooth angle of 55 ° and a thread with a taper of 1:16. This series of threads is widely used in the world. Its code name and regulations in different countries are different, see the table below. According to the foreign code in the table below, it will be converted into the code of our country.
Country code
China ZG, R (external thread)
British BSPT, R (external thread), Rc (internal thread)
France G (external thread), R (external thread)
Germany R (external thread)
Japan PT, R
ISO R (external thread), Rc (internal thread)
4. Conversion of 60 ° conical pipe thread
The 60 ° conical pipe thread refers to a pipe thread with a tooth angle of 60 ° and a thread taper of 1:16. This series of threads is used in China's machine tool industry and the United States and the former Soviet Union. Its code name, which was previously stipulated as K in our country and later as Z, is now changed to NPT. The thread code comparison table is shown in the table below.
Country code
China Z (Old) NPT (New)
United States NPT
Soviet Union B
5. Conversion of 55 ° trapezoidal thread
Trapezoidal thread refers to a metric trapezoidal thread with a tooth angle of 30 °. This series of threads is relatively uniform at home and abroad, and their code names are also quite consistent.
Country code
China T (old) Tr (new)
ISO Tr
Germany Tr
Former Soviet Union Tr
Thread classification
It can be divided into:
1. International Metric Thread System
The thread adopted by China's national standard CNS. The top of the tooth is flat and easy to turn, and the bottom of the tooth is rounded to increase the thread strength. The thread angle is 60 degrees, and the specification is indicated by M. Metric threads can be divided into coarse and fine teeth. The notation is M8x1.25. (M: code, 8: nominal diameter, 1.25: pitch).
2. American Standard Thread (American Standard Thread)
Both the top and the root of the thread are flat, and the strength is better. The thread angle is also 60 degrees, and the specifications are expressed in terms of how many teeth per inch. This thread can be divided into coarse teeth (NC); fine teeth (NF); extra fine teeth (NEF) three levels. Notation is like 1 / 2-10NC. (1/2: outer diameter; 10: number of teeth per inch; NC code).
3. Unified Thread
It is jointly formulated by the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada, and is the commonly used British thread.
The thread angle is also 60 degrees, and the specifications are expressed in terms of how many teeth per inch. Such threads can be divided into coarse teeth (UNC); fine teeth (UNF); extra fine teeth (UNEF). The notation is 1 / 2-10UNC. (1/2: outer diameter; 10: teeth per inch; UNC code)
4. V-shaped thread (Sharp VThread)
The top and the root are pointed, and the strength is weak, and it is not easy to use. The thread angle is 60 degrees.
5. Whitworth Thread
The thread adopted by the British National Standard. The thread angle is 55 degrees, indicating that the symbol is "W". Suitable for rolling method manufacturing. The notation is as W1 / 2-10. (1/2: outer diameter; 10: teeth per inch; W code).
6, round thread (KnuckleThread)
It is the standard thread set by German DIN. Suitable for the connection of bulbs and rubber tubes. The symbol is "Rd".
7. Pipe thread (PipeThread)
In order to prevent leakage, the thread is often used to connect gas or liquid pipe fittings. The thread angle is 55 degrees, which can be divided into straight pipe thread code "P.S., N.P.S." and inclined pipe thread code "N.P.T.", its taper is 1:16, that is, 3/4 inch per foot.
8. Square Thread (SquareThread)
The transmission efficiency is large, second only to the ball thread, and it cannot be adjusted with a nut after wear, which is a disadvantage. Generally used for the screw of the vise and the thread of the crane.
9. Trapezoidal thread
Also known as Arkham thread. The transmission efficiency is slightly smaller than the square thread, but the nut can be adjusted after wear. The thread angle of the metric system is 30 degrees, and that of the inch system is 29 degrees. Generally used for lead screw of lathe. The symbol is "Tr".
10.Zigzag thread (ButtressThread)
Also known as rhombic thread, it is only suitable for unidirectional transmission. Such as screw jacks, presses, etc. The symbol is "Bu".
11. Ball thread
It is the thread with the best transmission efficiency, which is difficult to manufacture and extremely expensive. It is used in precision machinery. Such as the lead screw of CNC machine tool.
Representation of inch bolts:
LH 2N 5/8 × 3-13UNC-2A
(1) LH is the left thread (RH is the right thread and can be omitted).
(2) 2N double thread.
(3) 5/8 inch thread, outer diameter 5/8 ".
(4) 3 The bolt length is 3 ”.
(5) 13 threads have 13 teeth per inch.
(6) UNC unified standard thread coarse teeth.
(7) Level 2 fit, external thread (3: tight fit; 2: medium fit; 1: loose fit) A: external thread (can be omitted) B: internal thread
Inch thread:
The size of the inch thread is usually expressed by the number of threads per inch of the thread, referred to as "number of teeth per inch", which is exactly equal to the reciprocal of the pitch. For example, a thread with 8 teeth per inch has a pitch of 1/8 inch.
|
 |
| Products Catalogue | Home | About Us | Retrofit | Download | News | Tech Support | Contact Us | |
|
|
|
