1 Description of the abnormal noise of the servo axis
Abnormal noise of the servo axis is a common problem in the factory debugging of the machine tool. The main manifestations are as follows:
(1) In a static state, the motor load fluctuates after the machine is powered on, and you can feel jitter or "buzzing" when you touch the motor with your hand;
(2) When the machine tool is in manual mode, the moving servo axis appears violently jittering or screaming;
(3) When the machine tool is in automatic mode, there is severe jitter or squeal when moving each axis for positioning;
(4) In the automatic mode of the machine tool, severe jitter or squealing occurs during interpolation of each axis;
(5) When the machine tool is in the automatic mode, there is a low impact sound during certain specific processing
(6) Other forms of abnormal noise occur during the operation of the machine tool
2 Reasons for abnormal noise of servo shaft
(1) Cause analysis of abnormal noise of semi-closed loop servo axis
In a semi-closed-loop controlled machine tool, the parameter setting is relatively simple. As long as the code of the motor is set, the system can automatically perform reasonable matching. Therefore, after initial setting, the machine tool can generally run smoothly and reliably.
Mechanical installation: In the semi-closed loop abnormal noise, in many cases, the vibration can be eliminated by adjusting the mechanical installation. The common mechanical links that cause abnormal noise are: coupling, bearing, screw, guard, etc. In these installation links, As long as the manufacturer assembles in accordance with the installation standards of each part, the abnormal shaft noise caused by the installation can be avoided.
Parameter setting: Unreasonable parameter setting will also cause abnormal noise of the axis. The specific setting method will be described in detail in the subsequent chapters.
(2) Analysis of the cause of abnormal noise of the fully closed loop servo axis
In a full-closed-loop machine tool, a grating ruler or encoder is usually used to achieve full-closed-loop control of the machine tool. While the full closed loop improves the accuracy of the machine tool, it also causes abnormal noise due to various factors, especially on large-scale machine tools. The common reasons for abnormal noise are as follows.
External interference: Usually, most of the connecting cables between the encoder, grating ruler and SDU module used in full closed-loop control are made by MTB itself, so the quality of the wire and the shielding cannot be well guaranteed, and the strong interference source outside the machine tool is relatively high. Many, interference often exists. Interference usually causes malfunctions of the servo axis, abnormal noise, and failure to establish the zero point. However, the problem can be solved by strengthening the shielding and standardizing the wiring, so I won't repeat it here.
Mechanical transmission: Under normal circumstances, the specifications of the fully closed-loop machine tool are medium and large, and the mechanical transmission is rack and pinion, large screw, etc. Usually equipped with a large reduction mechanism, most of the mechanical transmission rigidity is not high, and the transmission gap is large, resulting in abnormal noise during the full-closed loop control.
Parameter setting: Unreasonable parameter setting will also cause abnormal noise of the axis. The specific setting method will be described in detail in the subsequent chapters.
3 Check points for abnormal noise of servo axis under semi-closed loop
(1) Gain adjustment
 
Increasing the position loop gain and speed gain of each axis can effectively improve the response performance of each axis and increase the rigidity of the machine tool. However, excessive gain will affect the stability of the machine tool and cause abnormal noise. By reducing the position gain and speed gain of the axis, the problem can be eliminated. Abnormal shaft noise caused by excessive rigidity.
(2) Servo frequency response adjustment
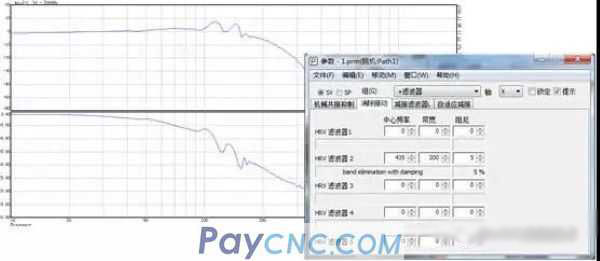
Frequency response adjustment in servo adjustment is one of the basic steps that need to be adjusted for machine tool servo optimization, and the specific debugging process will not be described in detail.
(3) TCMD current measurement
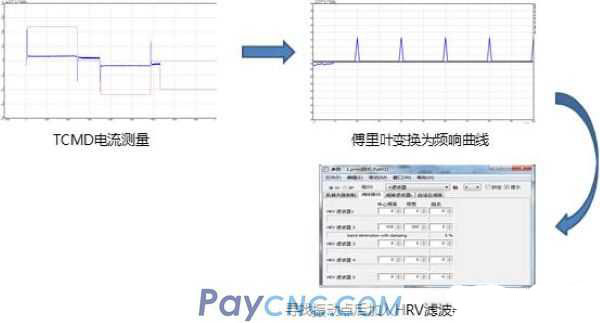
After the frequency response is measured, if the axis still has abnormal noise during G00 positioning or G01 single-axis interpolation or multi-axis interpolation, then you can perform TCMD current measurement to determine the vibration point.
(4) Other forms of abnormal noise treatment
The previous methods can basically solve the problem of abnormal noise and squeal of the axis, and the unreasonable servo parameter setting will also cause abnormal noise or impact noise in the operation of the machine tool.
a. Abnormal noise when the machine is stopped
When the machine is at a standstill, the motor has abnormal noise, and when the load jumps greatly, the following methods can be used to eliminate the vibration:
1. Measure the TCMD curve at rest, find the vibration point through Fourier change, and eliminate the vibration through HRV or TCMD filter.
2. Use the variable gain function when stopped.
 
3. Check whether the speed loop proportional high-speed processing function is used. This function can make the proportional calculation of the speed control faster and improve the accuracy, but the low-frequency mechanical vibration will be amplified, resulting in abnormal noise when stopping

4. Use acceleration feedback function This function is a compensation for speed loop feedback. Because the transmission link of the machine tool causes elastic deformation, or the inertia of the load is converted to the motor shaft and is larger than the rotor inertia of the motor, an oscillation of 50-150 Hz will occur. Use this function to compensate the feedback during acceleration, speed up the response and eliminate shocks. Generally set between -10 and -20. If there is vibration during acceleration and deceleration, this parameter value can be appropriately reduced. It should be noted that if this value is too large, it may cause abnormal noise.

5. Check whether the current loop 1/2PI function is used. This function can improve the current loop response, but it may cause the excitation sound of the motor to increase when stopping or abnormal noise when stopping.

b. Abnormal noise when the machine axis is running
When the machine is in a static state, the motor has abnormal noise when it is started. When the load jumps greatly, the following methods can be used to eliminate the vibration:
1. When the static friction of the machine tool is large, the crawling phenomenon may occur during the starting process and cause abnormal noise. At this time, the N pulse suppression function can be used to eliminate the vibration.

2. The abnormal noise is started by the handwheel, and the abnormal noise can be slowed by increasing the 1624 manual time deceleration time constant.

3. The abnormal shaft noise caused by the impact of the motor during the G00 positioning of the machine tool can be eliminated by adjusting 1620, 1621 or 1671, 1672.
4. Abnormal noise occurs during processing in automatic mode, you can check whether the processing related parameters are set reasonably, whether the acceleration/deceleration method is linear, etc.
4 Check points for abnormal noise of servo axis under full closed loop
After processing the semi-closed loop abnormal sound, if there is abnormal sound in the full closed loop, the main reason is the external interference and the installation accuracy of the detector. There are mainly the following methods for parameter processing
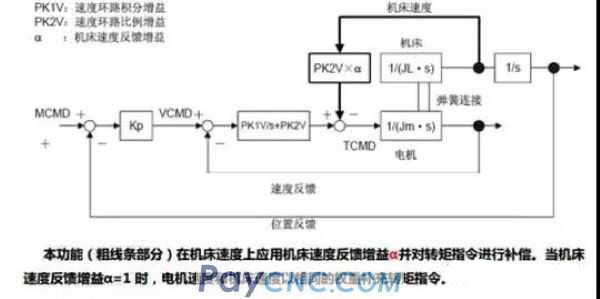
(1) Machine speed feedback function
The speed of the machine tool itself is added to the speed control zone in a fully closed loop system, thereby ensuring the stability of the entire position loop and reducing vibration
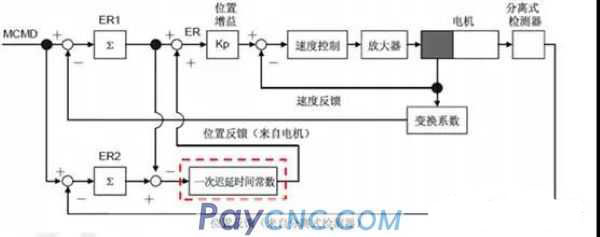
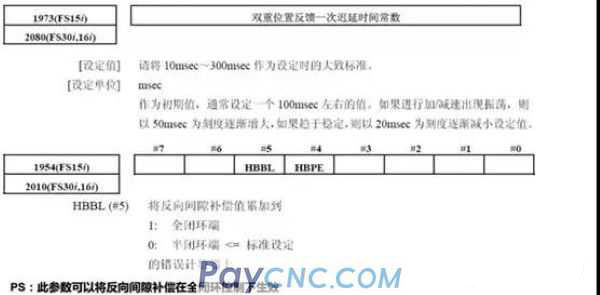
(2) Dual position feedback function
The dual position feedback function is to consider the position data of the full closed loop and the semi-closed loop at the same time, and control the full closed loop into a function similar to the semi-closed loop.
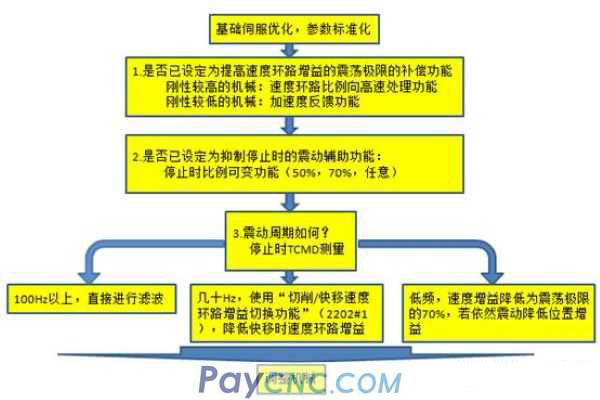
Servo shaft abnormal noise processing process
(1) Abnormal sound when stopped
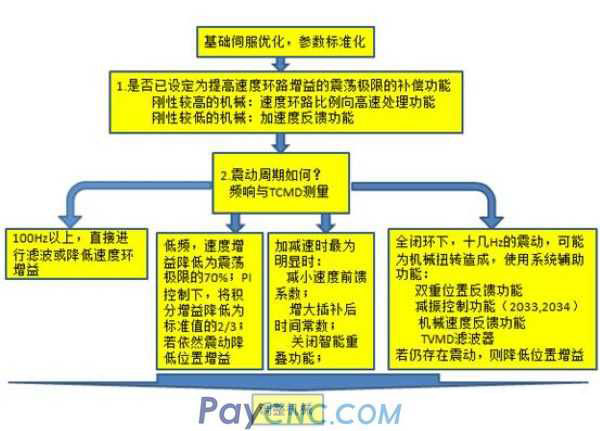
(2) Abnormal noise during exercise
 |
 |
| Products Catalogue | Home | About Us | Retrofit | Download | News | Tech Support | Contact Us | |
|
|
|
